The Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger market plays a crucial role in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning). As these industries continue to evolve, so too does the demand for more efficient, durable, and cost-effective heat exchangers. One of the key areas of focus for industry innovators is the development of advanced materials that improve the performance and lifespan of Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger (STHE) Market. This article delves into recent innovations in materials and coatings that enhance corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and overall durability.
Understanding Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers
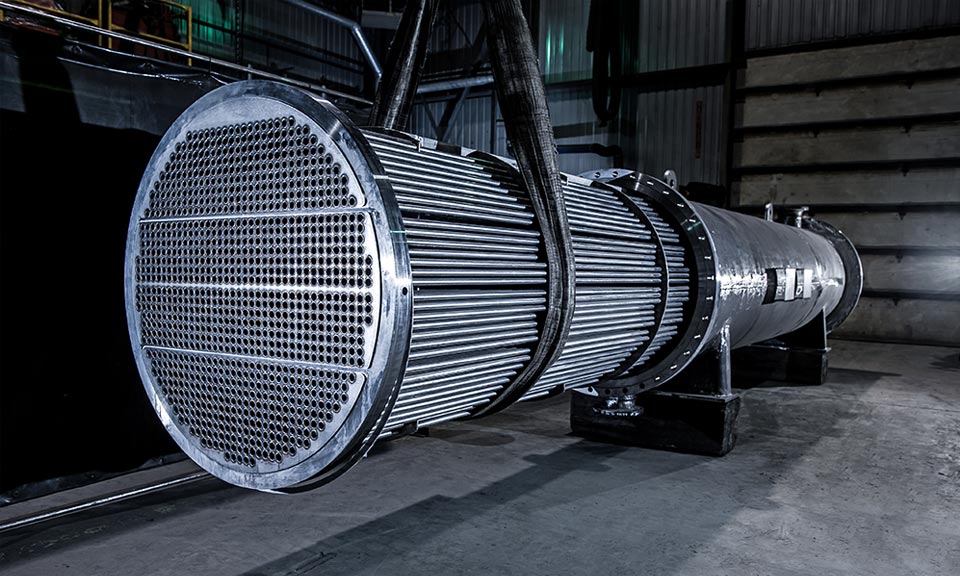
A Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger (STHE) consists of a series of tubes, one set of which carries the hot fluid, while the other carries the cold fluid. Heat transfer occurs through the walls of the tubes, facilitating the cooling or heating of the respective fluids. They are essential in maintaining thermal balance across a wide range of industrial applications. As industries become more demanding in terms of operational efficiency, the focus is shifting towards improving the materials that make up these exchangers to maximize performance while minimizing downtime for maintenance.
The Challenge: Corrosion Resistance and Durability
One of the primary challenges faced by Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers is their susceptibility to corrosion. Given the extreme temperatures and pressures that heat exchangers are subjected to, materials used must exhibit high corrosion resistance and ability to withstand harsh environments. Corrosion not only reduces the lifespan of the heat exchanger but can also lead to system failures, causing production losses and additional maintenance costs.
Advancements in Alloy Materials
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in alloy materials used in Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers. New alloys offer better performance in terms of corrosion resistance, strength, and thermal conductivity. These advanced materials allow heat exchangers to function at higher efficiency levels, even in the most demanding conditions.
Stainless Steel Alloys
Stainless steel has been a popular choice for heat exchangers due to its high corrosion resistance and strength. However, new grades of stainless steel have been developed to further enhance these properties. For instance, duplex stainless steels, which offer a combination of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, provide superior corrosion resistance, especially in environments where chloride-induced corrosion is a concern. These alloys are increasingly being used in industries such as chemical processing and oil & gas, where exposure to corrosive fluids is common.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are another material gaining traction in the Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger market. Titanium is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in seawater and other aggressive environments. It also boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for applications where weight and strength are critical factors. Additionally, titanium alloys can operate effectively in high-temperature environments, making them suitable for power generation and petrochemical applications.
Nickel-Based Alloys
Nickel-based alloys, particularly those containing molybdenum and copper, offer outstanding resistance to corrosion, especially in highly acidic or seawater environments. These materials are commonly used in the oil and gas industry, where extreme conditions, such as high pressure and high temperatures, are prevalent. Nickel alloys are particularly effective in preventing stress corrosion cracking and pitting, two common issues faced by heat exchangers.
Coatings for Enhanced Performance
While advanced alloys have significantly improved the performance of Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers, the application of specialized coatings further enhances the material properties, making these exchangers more durable and efficient. Coatings provide an additional layer of protection against corrosion, fouling, and wear, extending the lifespan of the equipment and reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings are gaining popularity due to their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. These coatings are particularly beneficial in heat exchangers exposed to aggressive fluids, such as acids and salts. Ceramic coatings not only improve corrosion resistance but also reduce friction, leading to better thermal efficiency. They are often used in conjunction with titanium or stainless steel alloys to provide a comprehensive protective layer.
Epoxy Coatings
Epoxy coatings are commonly used to protect heat exchanger tubes from corrosion caused by exposure to water and other chemicals. These coatings offer excellent resistance to chemical attack and can be tailored to suit specific industrial applications. Epoxy coatings are ideal for environments where the heat exchanger will be exposed to harsh fluids, such as those in the chemical or food processing industries. They also help reduce biofouling, improving the heat exchanger's overall efficiency.
Nanocoatings
Nanotechnology is an emerging area in material science, and its application in heat exchangers is an exciting development. Nanocoatings, which consist of materials engineered at the nanoscale, offer superior properties compared to traditional coatings. They can provide increased resistance to wear, corrosion, and fouling, all of which are crucial for maintaining the efficiency of Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers. Nanocoatings can also enhance heat transfer properties by increasing the surface area of the heat exchanger, leading to improved performance in heat exchange processes.
Thermal Conductivity: The Role of Materials
The efficiency of a Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger is largely determined by its thermal conductivity—the ability of the material to conduct heat. In the past, materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper, were widely used. However, as industries demand higher efficiency and greater resistance to corrosion, new materials are being explored to strike a balance between thermal conductivity and other critical properties.
Copper Alloys
Copper remains one of the most efficient materials in terms of thermal conductivity. However, its susceptibility to corrosion in certain environments limits its use in heat exchangers. To overcome this, copper alloys that include elements such as tin or nickel are being used. These alloys offer improved corrosion resistance while maintaining the thermal conductivity benefits of copper. These alloys are particularly useful in the HVAC and refrigeration industries, where efficient heat transfer is essential.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum is another material that offers excellent thermal conductivity while being lightweight and resistant to corrosion. However, its strength can be a limiting factor in high-pressure applications. New aluminum alloys with added elements such as manganese and silicon offer improved strength and corrosion resistance without compromising thermal performance. These alloys are becoming more prevalent in applications such as automotive and aerospace industries, where weight reduction is important without sacrificing thermal efficiency.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger Materials
The Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger market is continuously evolving, with material innovation at the forefront of this transformation. As industries push the boundaries of performance, new materials and coatings will play a key role in meeting these demands. Future trends are likely to focus on further enhancing thermal conductivity, improving corrosion resistance, and extending the lifespan of heat exchangers through the development of new alloys and nanocoatings.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
In addition to improving efficiency and performance, there is an increasing emphasis on sustainability in the Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger market. As industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste, the demand for environmentally friendly materials is growing. The use of recyclable alloys and coatings, as well as the development of energy-efficient heat exchangers, aligns with global efforts to create more sustainable industrial solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, advancements in Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger materials, including innovative alloys and coatings, are driving the market towards greater durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. These materials, from stainless steel and titanium to cutting-edge nanocoatings, offer improved corrosion resistance, enhanced thermal conductivity, and extended operational lifespans. As industries continue to push for higher performance standards, the development of new materials will play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers, ultimately contributing to more sustainable industrial processes.




Comments