Introduction:
The healthcare industry is in the midst of a technological transformation, with medical robotics emerging as one of the most promising fields in improving patient care and outcomes. The rapid advancement of robotic technologies in healthcare is reshaping how surgeries, diagnostics, patient care, and rehabilitation are delivered. With the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and advanced sensors, robotic systems are offering greater precision, efficiency, and safety. From robotic surgery systems to automated rehabilitation tools, the range of applications for medical robots is vast. Among the many benefits of medical robotics, one of the most impactful is its role in infection control in hospitals, which is essential in enhancing patient safety and improving healthcare outcomes. This article will explore the latest trends in medical robotics, particularly focusing on how robotic systems are revolutionizing healthcare and contributing to infection control in hospitals.
Download FREE Sample of Artificial Intelligence Market: https://www.nextmsc.com/artificial-intelligence-market/request-sample
The Rise of Medical Robotics in Healthcare
Medical robotics has grown rapidly over the past few decades, driven by advances in technology and a growing need for more efficient, accurate, and minimally invasive treatments. Robotics technologies have been adopted across a wide range of healthcare areas, including surgery, rehabilitation, diagnostics, and infection prevention. Robotic systems have become integral to improving healthcare delivery, allowing healthcare providers to perform complex tasks with greater precision and effectiveness.
The demand for minimally invasive procedures, such as robotic-assisted surgeries, is increasing due to the many advantages these systems offer, including reduced patient recovery times, fewer complications, and more precise outcomes. These benefits are just the beginning, as robots are now being designed to assist not only in surgeries but also in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and infection control. One key area where robots have demonstrated their potential is infection control, an issue that remains a major concern in healthcare facilities worldwide.
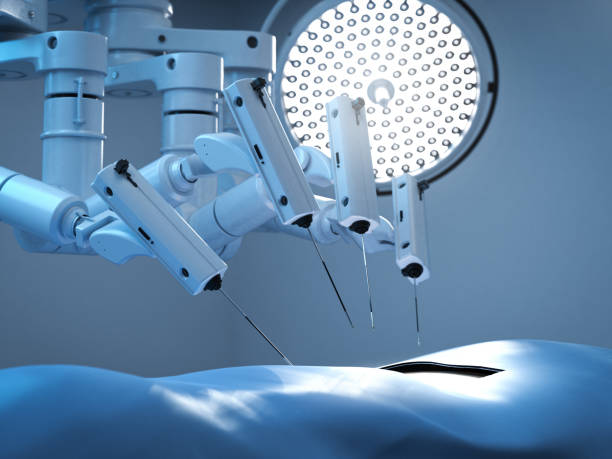
Robotic Surgery: Precision and Efficiency
One of the most widely recognized applications of medical robotics is robotic-assisted surgery. Robotic surgery systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, are helping to redefine surgery by enabling highly precise procedures with minimal invasiveness. These robotic systems allow surgeons to make smaller incisions, resulting in reduced risk of infection, less blood loss, and shorter recovery times for patients.
The precision offered by robotic surgery systems is particularly crucial in complex procedures, such as those involving delicate tissues, organs, and structures. With enhanced visualization and the ability to scale fine movements, robotic systems allow surgeons to perform procedures with much greater accuracy than traditional methods. This leads to better patient outcomes and a reduction in complications, including infections, which can arise from open surgeries.
Robotic systems have also contributed to reducing the occurrence of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) by minimizing the need for large surgical incisions and reducing human error. These systems, equipped with advanced imaging technology, enable the surgeon to operate in a more controlled environment with greater precision, significantly reducing the risks associated with traditional surgeries.
The Role of Robotic Systems in Infection Control in Hospitals
Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) remain one of the most significant challenges in healthcare. Infections acquired during hospital stays can complicate recovery, extend hospital stays, and, in some cases, even result in death. Controlling infections in a hospital setting is crucial to improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. Robotic systems are emerging as an essential tool in preventing and controlling infections within healthcare environments.
One of the primary ways robots are addressing infection control is through the use of autonomous disinfection systems. These robots use ultraviolet (UV) light, hydrogen peroxide vapor, or other sterilizing methods to disinfect hospital rooms, operating theaters, and other patient care areas. Automated disinfection robots, such as Xenex’s LightStrike robots, have been shown to effectively reduce the presence of pathogens like Clostridium difficile, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and other harmful microorganisms that contribute to infections.
These robotic disinfection systems are particularly valuable because they provide consistent, thorough cleaning, which can be difficult to achieve with manual cleaning alone. Unlike human cleaners, robots can disinfect spaces more efficiently, without missing hard-to-reach areas, and can be programmed to clean rooms quickly and effectively between patient visits. This reduces the likelihood of cross-contamination between patients and prevents the spread of hospital-associated infections.
Moreover, autonomous disinfecting robots also help reduce healthcare workers’ exposure to hazardous cleaning chemicals and toxic pathogens, creating a safer environment for staff as well as patients. These robots offer a highly efficient, safe, and non-invasive way to maintain high standards of infection control in healthcare settings.
Robots in Sterile Environments: Preventing Contamination
Sterile environments, such as operating rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), and isolation rooms, are essential for maintaining patient safety, particularly during surgical procedures and the treatment of immunocompromised patients. Robotic systems are playing an important role in ensuring these environments remain free from contaminants.
Robots are increasingly being used to transport medical equipment, medications, and supplies without exposing them to contamination. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robots designed for material handling can deliver sterile supplies, surgical tools, and medications without human interaction, thereby reducing the risk of contamination and infection. These robots navigate hospital corridors and rooms autonomously, using Sensors and AI to avoid obstacles and ensure timely and safe delivery of essential items.
Download FREE Sample of Sensors Market: https://www.nextmsc.com/sensor-market/request-sample
In addition to transportation, robots are also used to monitor the cleanliness of these environments. With built-in sensors, robots can check air quality, temperature, humidity, and contamination levels, ensuring that all variables are within acceptable ranges to prevent the growth and spread of infectious pathogens.
Enhancing Patient Safety and Infection Prevention with Robotic Assistance
Robotic systems are not only helping to prevent infections through disinfection and sterilization but also by reducing human involvement in tasks that may lead to the spread of germs. For example, robots used in surgeries or diagnostic procedures provide a more sterile operating environment by reducing the number of personnel interacting directly with patients and medical instruments. This limits human contact and thus reduces the likelihood of contamination during sensitive procedures.
Additionally, medical robots are increasingly used in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to interact with patients from a distance. Robotic telepresence systems enable doctors and nurses to conduct virtual consultations with patients, reducing the need for in-person interactions that may inadvertently expose patients to pathogens. These telehealth robots can also monitor patient vital signs remotely, helping to track recovery progress without the need for physical contact, thus reducing infection risks.
The Impact of AI and Machine Learning in Infection Control
AI and machine learning are integral components of modern medical robotics, enhancing their capabilities and effectiveness in infection control. AI algorithms can help robots analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might not be immediately apparent to healthcare workers. For example, AI-powered robots can use data from sensors to detect areas in need of cleaning or to identify contamination risks before they escalate.
Machine learning enables robotic systems to improve over time by learning from their environment and experiences. By analyzing data from previous cleaning cycles, robotic disinfection systems can optimize their disinfection patterns, ensuring that high-risk areas receive the most attention. This leads to more efficient infection control and an overall reduction in the spread of harmful pathogens in healthcare settings.
Moreover, AI can assist in the predictive analysis of infection outbreaks by analyzing trends in infection rates, patient data, and environmental factors. With this predictive capability, healthcare facilities can better prepare for potential outbreaks and implement proactive measures to control infections before they spread.
The Future of Robotics in Infection Control and Healthcare
The future of robotics in healthcare is poised to further enhance infection control practices. As robotic systems become more advanced, we can expect to see robots that are capable of conducting a broader range of tasks to prevent infections, from cleaning to monitoring and even diagnostics. Additionally, the continued integration of AI and machine learning will enable robots to become even smarter, more adaptable, and more effective at preventing hospital-acquired infections.
With ongoing advancements in robotics, hospitals will likely see a reduction in both infection rates and the overall spread of disease. The development of more autonomous, efficient, and cost-effective robots will ensure that infection control remains a top priority in hospitals and healthcare settings around the world.
Conclusion
Medical robotics is revolutionizing healthcare by offering new solutions that improve precision, efficiency, and safety. Robotic systems are playing an increasingly vital role in infection control by automating disinfection, reducing human contact, and monitoring sterile environments. These technologies help healthcare providers maintain high standards of hygiene and reduce the spread of hospital-acquired infections, ultimately enhancing patient safety and improving healthcare outcomes. As the technology continues to evolve, the role of robotics in infection control will only grow, making healthcare environments safer for both patients and medical staff. The future of healthcare is becoming increasingly robotic, with innovation paving the way for safer, more efficient care across the globe.
Read the complete blog: https://www.nextmsc.com/blogs/medical-robotics-market-trends




Comments