In minimally invasive surgery, specimen retrieval bags are essential tools for safely collecting and removing specimens from the body. However, selecting the appropriate trocar size for the procedure is critical to ensuring the effectiveness of the specimen retrieval bag and preventing complications.
This article delves into the relationship between trocar size and specimen retrieval bags, highlighting key considerations and offering expert insights for surgeons and medical professionals.
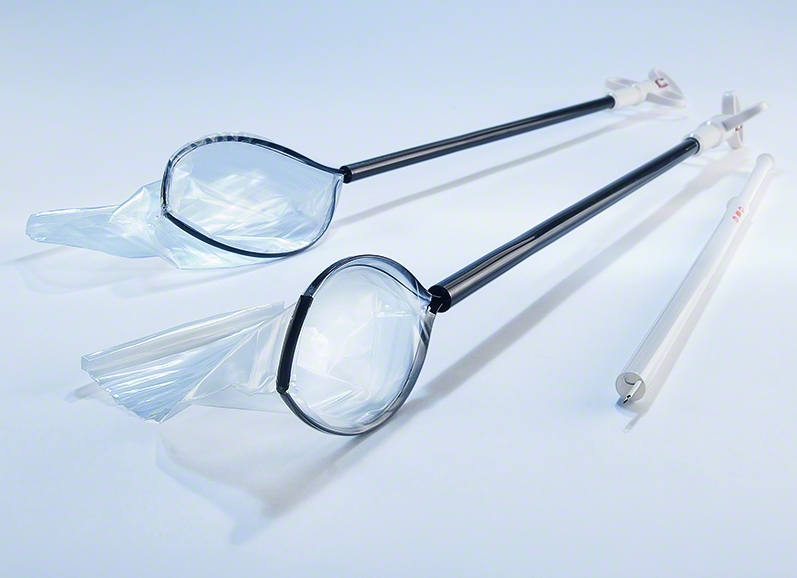
What is a Specimen Retrieval Bag?
A specimen retrieval bag is a medical device used during laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery to safely capture and remove tissue samples or surgical specimens from the body. These bags come in various sizes and designs, tailored to suit the nature of the surgery, the type of specimen, and the trocar size used for the insertion.
Specimen retrieval bags are typically made from soft, flexible materials such as medical-grade nylon or polymer, allowing them to expand and contract to accommodate specimens of varying sizes. During laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon uses a trocar to create an entry point in the abdominal cavity. The retrieval bag is inserted through the trocar to contain and remove specimens.
Why is Trocar Size Important?
The size of the trocar plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of a specimen retrieval bag during laparoscopic procedures. The trocar creates a passageway for the insertion of surgical instruments, including the specimen retrieval bag, into the body. If the trocar is too small, the bag may not fit, making it difficult or impossible to retrieve specimens safely. On the other hand, if the trocar is too large, it can increase the risk of injury to the surrounding tissues and organs.
Selecting the right trocar size ensures that the specimen retrieval bag can be inserted and deployed effectively without compromising the safety of the patient. It also ensures that the bag can securely contain the specimen without the risk of rupture or loss during extraction.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Trocar Size for Specimen Retrieval Bag
1. Type of Surgery
The type of surgery being performed will influence the choice of trocar size. For example, in gynecological surgeries such as laparoscopic hysterectomy or myomectomy, smaller trocars (usually 5mm or 10mm) may be sufficient for inserting smaller retrieval bags. However, in larger procedures, such as colectomies or cancer surgeries, a larger trocar may be needed to accommodate larger retrieval bags and specimens.
2. Size of the Specimen
The size of the specimen is another determining factor when selecting the trocar size. Smaller specimens, such as tissue samples or small tumors, require smaller retrieval bags and, consequently, smaller trocars. Larger specimens, such as whole organs or larger tumors, require larger retrieval bags that necessitate larger trocars for insertion.
A specimen retrieval bag should be large enough to safely contain the specimen, but not so large that it cannot be deployed or retrieved through the trocar. The bag’s size must correspond with the trocar’s internal diameter to ensure a smooth, effective retrieval process.
3. Type of Specimen Retrieval Bag
Specimen retrieval bags come in different types, such as single-use or reusable bags, and various designs (e.g., circular, oval, or pouch-shaped). Some bags are designed with specific features to enhance safety and ease of retrieval, such as one-way valves or non-absorbable materials. The design and structure of the bag may impact the trocar size needed for insertion.
In some cases, specialized retrieval bags may be required for specific types of specimens, such as gallstones or large bowel segments, which could necessitate a larger trocar and bag combination.
4. Surgical Technique
The surgical technique used may also influence the trocar size. In laparoscopic surgeries, surgeons often prefer to use a technique called "bladed trocar insertion" or "non-bladed trocar insertion." Bladed trocars are typically larger in size and may require larger specimen retrieval bags, while non-bladed trocars are smaller and may be used with smaller retrieval bags. In addition, some surgeons may use a "hand-assisted" laparoscopic technique, where the trocar size may be larger, and a larger retrieval bag is required for specimen removal.
Common Trocar Sizes and Their Corresponding Retrieval Bags
1. 5mm Trocar
The 5mm trocar is often used for small-scale laparoscopic procedures, such as diagnostic laparoscopy or minor gynecological surgeries. For these surgeries, a smaller specimen retrieval bag is typically used, with sizes ranging from 6 to 10 cm. The 5mm trocar is usually sufficient to accommodate a small specimen retrieval bag without any difficulty.
2. 10mm Trocar
The 10mm trocar is the most commonly used size in laparoscopic surgeries and is suitable for a wide variety of procedures. This size allows for a slightly larger retrieval bag, which can be used for collecting tissue samples, small organs, or larger surgical specimens. A 10mm trocar typically pairs well with specimen retrieval bags ranging from 12 to 20 cm.
3. 12mm and 15mm Trocars
Larger trocars, such as the 12mm or 15mm, are often required for major surgeries, such as colectomies, cancer resections, or multi-organ removal. These larger trocars accommodate larger specimen retrieval bags (20 cm and above), which are capable of handling larger specimens like whole organs or large tumor masses. Larger trocars are also used in situations where the specimen must be manipulated or handled delicately, such as in cancer surgeries where the specimen must remain intact.
How to Ensure Proper Fit for Safe Retrieval
To ensure the safe and effective use of specimen retrieval bags, it is essential to select a trocar that provides the correct fit. The internal diameter of the trocar should be larger than the bag's folded diameter to ensure that the retrieval bag can pass through the trocar without difficulty. However, it should not be too large, as this could create unnecessary gaps and risk injury to surrounding tissues.
The retrieval bag should be introduced carefully through the trocar, ensuring that it is securely deployed inside the abdominal cavity. Surgeons should be familiar with the features of the specific retrieval bag being used, including its locking mechanisms and one-way valve functionality, to avoid complications during specimen collection.
Conclusion
The correct selection of trocar size when using a specimen retrieval bag is vital to ensuring the safety and success of laparoscopic surgeries. By considering the type of surgery, size of the specimen, and appropriate bag dimensions, surgeons can choose the ideal trocar size to prevent complications and ensure an effective procedure. With the right equipment and expert knowledge, the use of specimen retrieval bags can enhance patient outcomes and surgical precision, making them a vital part of modern minimally invasive surgery.




Comments