The New Frontier Of Medical Diagnostics: Technology And Innovation

Medical diagnostics is the cornerstone of modern healthcare, providing critical information that helps in the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases. From traditional laboratory tests to cutting-edge imaging techniques, advancements in medical diagnostics have significantly improved patient outcomes, enhanced disease prevention, and facilitated the development of personalized medicine. This blog delves into the various aspects of medical diagnostics, highlighting the transformative role of technology and the emerging trends shaping the future of this essential field.
Here are the Top 4 Aspects of Medical Diagnostics:
1. The Evolution of Medical Diagnostics
Medical diagnostics has come a long way since the days of rudimentary physical examinations and basic laboratory tests. The evolution can be broadly categorized into several phases:
- Pre-Laboratory Era: Early diagnostics relied heavily on physicians’ observations and patient-reported symptoms. Physical examinations, including palpation, auscultation, and inspection, were the primary tools for diagnosing illnesses.
- Laboratory Revolution: The advent of laboratory-based diagnostics marked a significant leap forward. Blood tests, urine analyses, and microbiological cultures became standard practices, providing more accurate and objective data.
- Imaging Techniques: The development of X-ray technology in the late 19th century revolutionized medical diagnostics. This was followed by advancements in ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, allowing for detailed visualization of internal structures.
- Molecular Diagnostics: The rise of molecular biology and genetics ushered in a new era of diagnostics. Techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation sequencing (NGS), and gene expression profiling enabled the identification of genetic mutations and biomarkers associated with various diseases.
- Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): The miniaturization of diagnostic devices and the development of rapid testing methods have made it possible to perform diagnostic tests at the patient’s bedside or in remote settings. This has improved accessibility and reduced turnaround times for results.
2. Cutting-Edge Technologies in Medical Diagnostics
Several advanced technologies are currently transforming the landscape of medical diagnostics. These innovations not only enhance the accuracy and speed of diagnosis but also open new avenues for early detection and personalized treatment.
a. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning

AI and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being integrated into diagnostic processes. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from medical images, electronic health records, and genetic profiles to identify patterns and predict disease outcomes. AI-powered diagnostic tools are particularly valuable in radiology, pathology, and genomics, where they assist in the detection of anomalies that might be missed by human eyes.
b. Liquid Biopsy
Traditional tissue biopsies can be invasive and painful for patients. Liquid biopsy is a less invasive alternative that involves analyzing blood samples to detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or other biomarkers. This technique is particularly useful for monitoring cancer progression, detecting minimal residual disease, and guiding personalized treatment plans.
c. Digital Pathology
Digital pathology involves the conversion of traditional glass slides into digital images that can be viewed, analyzed, and shared electronically. This technology facilitates remote consultations, improves workflow efficiency, and enhances the accuracy of diagnoses through advanced image analysis software.
d. Wearable Health Devices
Wearable health devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, continuously monitor physiological parameters like heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels. These devices provide real-time data that can be used for early detection of abnormalities and chronic disease management.
e. Infrared Thermography
Infrared thermography is a non-invasive imaging technique that detects heat patterns and blood flow in body tissues. This technology is used in various medical applications, including the detection of breast cancer, monitoring of musculoskeletal injuries, and assessment of vascular diseases. The Infrared Thermography industry is witnessing rapid growth due to its versatility and effectiveness in clinical diagnostics.
3. The Role of Medical Diagnostics in Disease Management

Effective disease management relies heavily on accurate and timely diagnostics. Here are some key areas where medical diagnostics play a crucial role:
1. Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection of cancer significantly improves survival rates. Diagnostic tools such as mammography, MRI, and PET scans are essential for detecting tumors at an early stage. Molecular diagnostics, including genetic testing and liquid biopsy, help in identifying specific mutations and tailoring targeted therapies.
2. Infectious Diseases
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of rapid and accurate diagnostics in managing infectious diseases. PCR tests, antigen tests, and serology tests were critical in detecting and tracking the spread of the virus. Similar diagnostic techniques are employed for diseases like HIV, tuberculosis, and influenza.
3. Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Diagnostic tools such as electrocardiograms (ECG), echocardiograms, and stress tests help in the early detection of heart conditions. Biomarker tests, including troponin and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), are crucial for diagnosing heart attacks and heart failure.
4. Genetic Disorders
Genetic testing is vital for diagnosing inherited disorders such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease. Advances in genomics have enabled the identification of genetic mutations responsible for these conditions, facilitating early intervention and genetic counseling.
4. The Future of Medical Diagnostics
The future of medical diagnostics is poised for remarkable advancements, driven by continuous innovation and integration of cutting-edge technologies. Here are some trends that are likely to shape the future:
a. Personalized Medicine
The concept of personalized medicine revolves around tailoring medical treatment to an individual’s unique genetic makeup and health profile. Advanced diagnostic tools, including genetic testing and molecular profiling, enable healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
b. Telemedicine and Remote Diagnostics
The integration of telemedicine with diagnostic technologies has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery. Remote diagnostics, facilitated by wearable devices and digital pathology, allow healthcare providers to monitor patients and diagnose conditions from a distance, improving accessibility and reducing healthcare costs.
c. Integration of Big Data and Healthcare Analytics
The vast amounts of data generated by diagnostic tests, electronic health records, and wearable devices present an opportunity for advanced analytics. Big data and healthcare analytics can identify trends, predict disease outbreaks, and optimize treatment strategies, ultimately enhancing patient care.
d. Expansion of the Infrared Thermography Industry
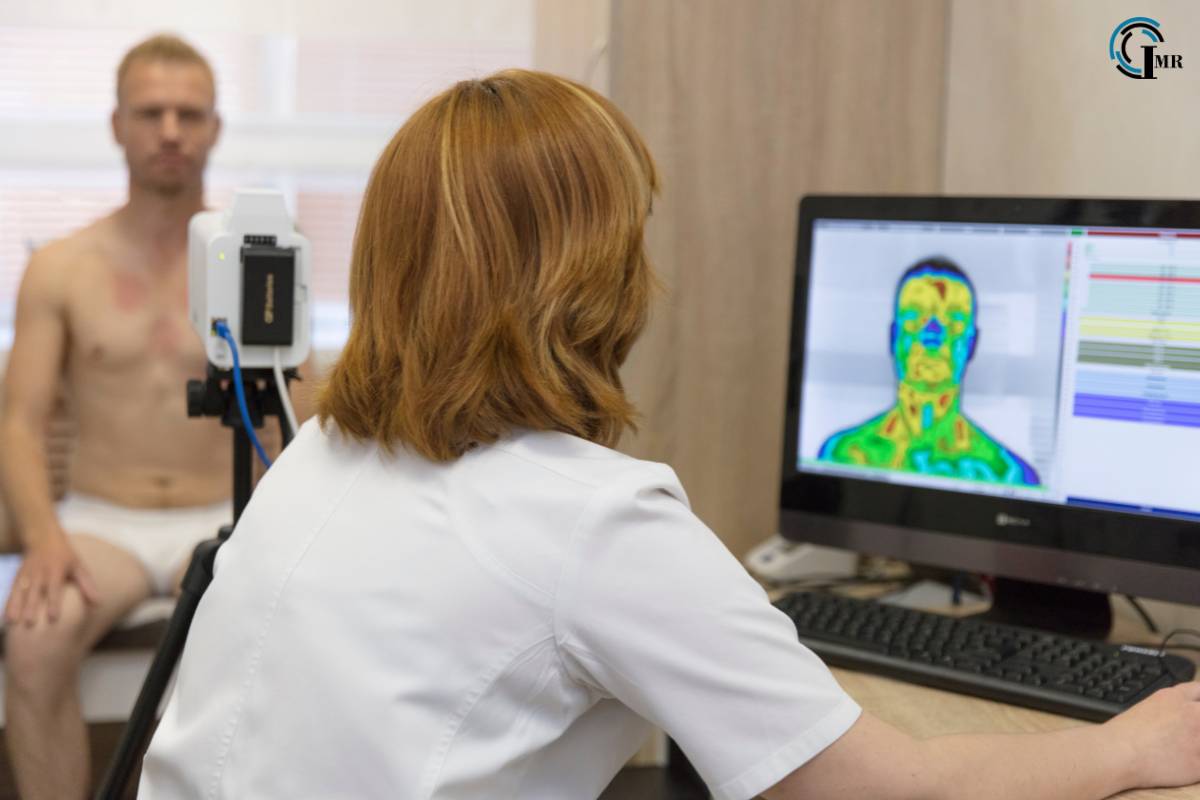
The Infrared Thermography industry is expected to expand further as the technology becomes more sophisticated and its applications in medical diagnostics continue to grow. Innovations in infrared sensors, image processing, and machine learning algorithms will enhance the accuracy and utility of infrared thermography in detecting various medical conditions.
e. Development of Novel Biomarkers
The discovery of novel biomarkers holds great promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and disease monitoring. Ongoing research in fields such as proteomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics is expected to yield new biomarkers that can be used for early detection and personalized treatment of diseases.
Conclusion
Medical diagnostics is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare. The integration of advanced technologies such as AI, liquid biopsy, digital pathology, and wearable devices has revolutionized the way diseases are detected, diagnosed, and managed. As the Infrared Thermography industry and other innovative diagnostic technologies continue to advance, the future of medical diagnostics holds immense potential for improving patient outcomes and transforming healthcare delivery. Embracing these advancements will not only enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostics but also pave the way for personalized and precision medicine, ultimately leading to better health and well-being for individuals worldwide.





Comments