Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a modern surgical technique that utilizes small incisions and specialized instruments to perform complex procedures. This approach offers a range of benefits compared to traditional surgery, including faster recovery times, reduced pain, and minimal scarring. As this technique continues to advance, more patients are choosing laparoscopic surgery for its effectiveness and convenience. This guide aims to provide comprehensive information about laparoscopic surgery, including the benefits, process, and outcomes, helping you make an informed decision if you’re considering this surgical option.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic Surgery in riyadh involves making small incisions, usually less than an inch long, through which a laparoscope and other specialized surgical tools are inserted. The laparoscope is a thin tube with a light and camera attached, which transmits high-definition images of the internal organs onto a monitor, allowing the surgeon to operate with precision. This technique can be applied to a wide range of procedures, from gallbladder removal to hernia repair, making it a versatile choice for various medical needs.
The Key Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Reduced Recovery Time
One of the main advantages of laparoscopic surgery is the significantly shorter recovery period. Since the procedure uses small incisions, there is less trauma to the body, allowing patients to resume their daily activities faster than with traditional surgery.
Minimal Scarring
Laparoscopic surgery leaves minimal scarring because of the small incisions used. Instead of large cuts, which can leave noticeable scars, patients have only a few tiny marks, making it a popular option for those concerned about post-surgical aesthetics.
Lower Risk of Infection
With smaller incisions, there is a reduced risk of infections post-surgery. Open surgeries, by contrast, expose the internal tissues more directly to the environment, increasing the chance of infections and other complications. Laparoscopic surgery helps minimize this risk.
Reduced Pain and Discomfort
Smaller incisions also result in less postoperative pain and discomfort. Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures generally require less pain medication, which reduces side effects and accelerates the overall recovery process.
Shorter Hospital Stays
Laparoscopic surgeries often allow patients to be discharged sooner than traditional surgeries, sometimes within a day. This not only saves costs associated with hospital stays but also improves the comfort of the recovery process as patients can heal in their own homes.
Common Procedures Using Laparoscopic Surgery
Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy)
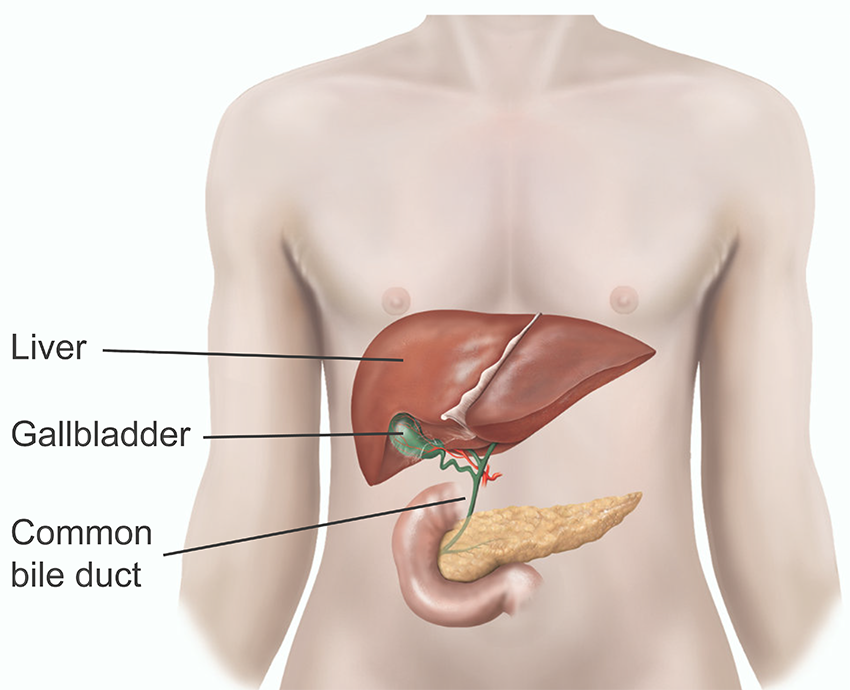
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is commonly performed to remove the gallbladder, especially in patients experiencing gallstones or gallbladder disease. This procedure is highly effective and offers a quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic surgery is frequently used to repair hernias, where tissue pushes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. This technique provides strong and lasting repairs, often with reduced pain and scarring.
Appendectomy
When the appendix becomes inflamed, laparoscopic appendectomy is an efficient way to remove it. The minimally invasive approach helps patients recover faster, allowing them to resume normal activities within days.
Weight Loss (Bariatric) Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is also used in bariatric procedures, including gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. These procedures can aid in significant weight loss and improve conditions related to obesity, such as diabetes and hypertension.
Gynecological Surgeries
Gynecological procedures like hysterectomies and ovarian cyst removals are commonly performed laparoscopically. This approach provides a less invasive option with quicker recovery times and reduced post-operative pain.
The Laparoscopic Surgery Process
Preoperative Preparations
Before undergoing laparoscopic surgery, patients usually need to undergo a series of evaluations. This may include blood tests, imaging, and consultations to ensure the patient’s readiness for the procedure. Additionally, patients are typically advised to avoid certain medications and follow fasting instructions before surgery.
Anesthesia Administration
Laparoscopic surgeries are usually performed under general anesthesia, which keeps the patient fully unconscious and ensures a painless procedure. An anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s vital signs throughout the operation to maintain safety.
Incision and Equipment Insertion
Once the patient is anesthetized, small incisions are made near the surgical site. Through these incisions, the surgeon inserts the laparoscope and other specialized instruments needed to perform the procedure. The camera provides real-time images on a monitor, guiding the surgeon with high precision.
Carbon Dioxide Insufflation
To create a clear view and provide space for surgical instruments, carbon dioxide gas is often pumped into the abdominal cavity. This inflation moves organs slightly apart, allowing the surgeon to navigate and operate with minimal interference.
The Surgical Procedure
The surgeon performs the necessary procedure, whether it’s removing an organ, repairing tissue, or any other required action. The laparoscopic tools provide the necessary control for a delicate and precise operation.
Closing the Incisions
Once the procedure is complete, the instruments are removed, and the carbon dioxide gas is released from the abdominal cavity. The incisions are then closed with stitches or small sutures, often leaving only a small mark.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Immediate Recovery Period
After laparoscopic surgery, patients are typically monitored in a recovery area for a few hours to ensure there are no immediate complications. Once stable, many patients are discharged on the same day.
Managing Postoperative Discomfort
Most patients experience mild soreness, especially near the incision sites. Pain management is usually straightforward, with over-the-counter medications often being sufficient. Your medical team will provide guidance on managing any discomfort.
Returning to Normal Activities
The recovery time after laparoscopic surgery is generally shorter than traditional surgery, with most patients resuming light activities within a few days. However, strenuous activities should be avoided for several weeks, depending on the specific procedure.
Postoperative Follow-Up
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled to assess the healing of incisions and address any concerns. This is also an opportunity to discuss any restrictions and ensure optimal recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
Infection Risk
While the risk of infection is lower in laparoscopic surgery, it is still possible. Signs of infection may include redness, swelling, or discharge around the incision sites. Immediate medical attention is advised if these symptoms appear.
Bleeding and Hematoma
In rare cases, bleeding can occur at the incision sites or internally. Surgeons take precautions to minimize this risk, but patients should be aware of symptoms like excessive bruising or abdominal pain.
Complications Related to Anesthesia
As with any procedure requiring anesthesia, there are some inherent risks, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions. An anesthesiologist assesses each patient’s health status before surgery to mitigate these risks.
Potential Organ Damage
Although uncommon, the instruments used in laparoscopic surgery can occasionally cause injury to nearby organs. Surgeons are highly trained to avoid this, and the risks remain minimal with skilled practitioners.
Expected Outcomes of Laparoscopic Surgery
Faster Return to Daily Life
One of the most anticipated outcomes is a quick return to daily life. Patients often find themselves resuming work and social activities much sooner than if they had undergone open surgery.
High Success Rates
Laparoscopic surgery has proven effective for a variety of medical conditions, often with high success rates. The minimally invasive approach yields favorable results with fewer complications.
Lasting Health Improvements
For patients with conditions like hernias or gallbladder disease, laparoscopic surgery often provides a long-term solution, relieving pain and improving quality of life.
Is Laparoscopic Surgery Right for You?
Laparoscopic surgery may be suitable for individuals who need surgical intervention but want to minimize recovery time and physical discomfort. It’s essential to discuss your medical history, current health status, and any potential risks with your healthcare provider. Understanding the benefits, risks, and outcomes of laparoscopic surgery can help you make an informed choice.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized modern medicine by offering a less invasive and highly effective approach to treating a wide range of medical conditions. With benefits such as reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications, it’s no surprise that laparoscopic surgery has become the preferred choice for many patients. This guide provides a comprehensive overview to help you understand what to expect from laparoscopic surgery, ensuring you can make a well-informed decision and confidently approach your treatment journey.




Comments