Bleeding gums are a common oral health problem that affects people of all ages. They often arise as a result of poor oral hygiene, but they can also be indicative of underlying health conditions. For most individuals, the initial symptom is a slight bleeding when brushing or flossing. This early sign should not be ignored, as untreated bleeding gums may lead to more severe dental and health issues. The key to preventing long-term damage lies in understanding the symptoms of bleeding gums and addressing the underlying cause promptly. If you're experiencing bleeding gums, it's essential to seek treatment for bleeding gums in Dubai(علاجًا لنزيف اللثة في دبي) at the earliest to prevent complications.
The Early Signs of Bleeding Gums:
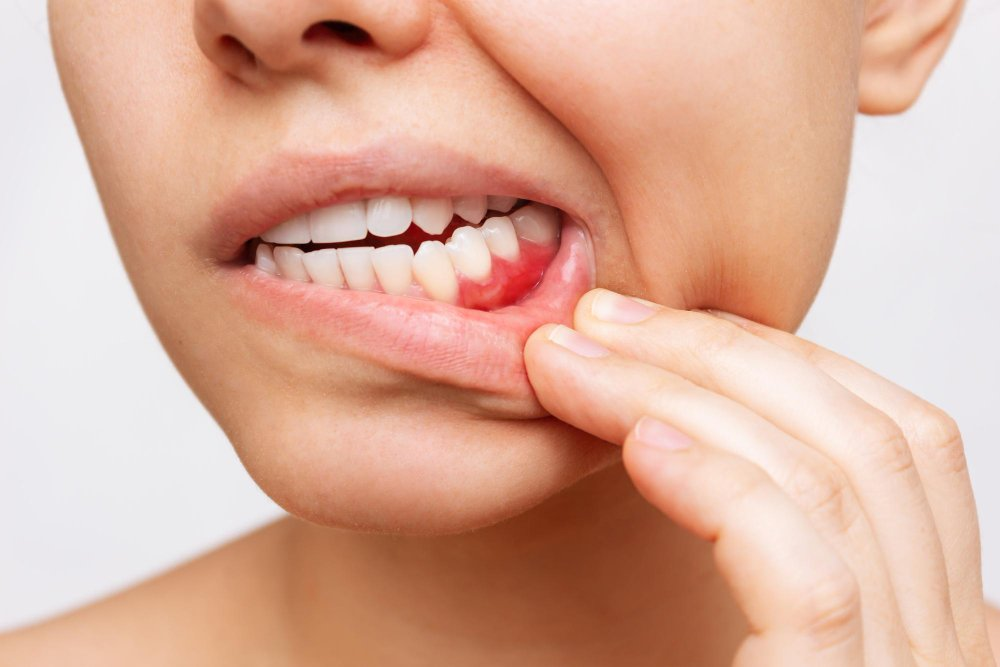
The first noticeable sign of bleeding gums is often a small amount of blood in the sink after brushing or flossing. Many people may overlook this symptom, assuming it’s a minor irritation. However, bleeding, even if minimal, can indicate the presence of gingivitis, which is the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis is caused by the accumulation of plaque on the teeth, which leads to inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, making it crucial to recognize this sign early and take action.
Bleeding while brushing or flossing can occur for various reasons, such as using a hard-bristled toothbrush or aggressive brushing techniques. However, persistent or recurring bleeding requires attention and should be investigated further.
Swelling and Redness of the Gums:
Another symptom of bleeding gums is swelling and redness around the affected area. Healthy gums are firm and pale pink, but when inflammation sets in due to plaque or bacterial build-up, the gums become swollen, tender, and red. Swollen gums may also feel soft and may cause discomfort or sensitivity, especially when eating or drinking. This redness and puffiness are classic indicators that the gums are irritated and may not be functioning properly. At this stage, the gums are vulnerable and should be treated to avoid the progression to periodontal disease.
In cases of severe gum disease, the swelling may become more pronounced, leading to visible changes in the shape of the gums. This can result in a noticeable gap between the gums and teeth.
Bad Breath (Halitosis) Linked to Bleeding Gums:
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth is another potential symptom that often accompanies bleeding gums. This condition, known as halitosis, can be caused by the build-up of bacteria in the mouth. When plaque and tartar accumulate along the gum line, bacteria begin to thrive, releasing unpleasant odors. The inflammation caused by gum disease exacerbates this issue, leading to foul-smelling breath. If you notice that your breath smells unusually bad or you have a bitter taste in your mouth, it could be a sign that bleeding gums are present.
Halitosis is often a secondary symptom that points to an underlying issue with your gums or teeth. Addressing the cause of gum bleeding will likely improve your breath and overall oral hygiene.
Pain or Discomfort While Eating:
As the gums become inflamed, individuals may begin to experience pain or discomfort, especially when eating certain foods. Hard or crunchy foods like apples, chips, or raw vegetables may feel especially painful due to the sensitivity of the gums. Additionally, hot or cold foods and drinks may irritate bleeding gums, causing sharp sensations or discomfort. This heightened sensitivity is due to the exposure of nerve endings within the gum tissue.
People with bleeding gums may also find that their gums bleed more easily when they chew or apply pressure. This sensitivity can also extend to the teeth, making brushing or even talking difficult.
Receding Gums: A Sign of Serious Gum Disease:
Receding gums, or the gradual pulling back of the gum line from the teeth, is another sign that your gums are unhealthy. When bleeding occurs regularly, it can lead to the weakening of the gum tissues, causing them to pull away from the teeth. This exposes more of the tooth and the root structure, increasing the risk of tooth decay and sensitivity.
Gum recession is often a sign of more advanced gum disease, such as periodontitis, which is a severe stage of gum disease that requires intervention to avoid tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to catch gum recession early and halt its progression.
Loose Teeth and Gum Pockets:
In more severe cases, bleeding gums can lead to loose teeth or the formation of gum pockets. Pockets are gaps between the teeth and gums where bacteria can accumulate. These pockets can become deep and difficult to clean properly, contributing to more bleeding and further damage to the gum tissue. Loose teeth can also occur as the gums weaken, losing their ability to securely hold teeth in place.
As the damage from gum disease increases, it may eventually lead to tooth mobility. Without proper treatment, tooth loss becomes a real possibility. This stage of gum disease is usually accompanied by deep, persistent gum bleeding, swelling, and tenderness around the affected teeth.
Prevention and Treatment for Bleeding Gums:
The most effective way to prevent bleeding gums is to maintain proper oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups are essential to catch potential issues early and prevent them from developing into more severe conditions.
While treatment for bleeding gums focuses on addressing the root cause—whether it be poor hygiene, a medical condition, or poor lifestyle habits—prevention through good oral hygiene is the best approach. Keeping your gums healthy can help prevent pain, swelling, and bleeding from returning, ensuring you maintain a strong and beautiful smile.





Comments