Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating beyond what is necessary for regulating body temperature. This condition can significantly impact daily life, leading to physical discomfort and emotional distress. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Hyperhidrosis Treatment in Dubai, including its causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and coping strategies.
What is Hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis is classified as a medical condition that leads to excessive sweating. While sweating is a normal bodily function that helps regulate temperature, hyperhidrosis occurs when the body sweats excessively without a clear cause, such as heat or physical exertion.
Types of Hyperhidrosis
There are two main types of hyperhidrosis:
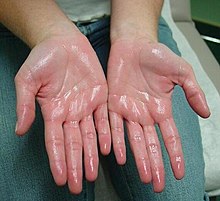
- Primary (Focal) Hyperhidrosis: This type typically affects specific areas of the body, such as the palms, soles of the feet, underarms, and face. It usually begins in childhood or adolescence and may be inherited.
- Secondary (Generalized) Hyperhidrosis: This type is less common and occurs due to an underlying medical condition or medication. It can affect the entire body and often starts in adulthood. Conditions that can cause secondary hyperhidrosis include thyroid problems, diabetes, menopause, and certain infections.
Causes of Hyperhidrosis
The exact cause of primary hyperhidrosis is often unknown, but it is believed to involve overactive sweat glands. In contrast, secondary hyperhidrosis has identifiable causes. Some common causes include:
- Medical Conditions: Hyperhidrosis can result from various medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, and infections.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antidepressants and blood pressure medications, can lead to excessive sweating as a side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menopause or puberty can trigger increased sweating.
- Emotional Triggers: Stress, anxiety, and embarrassment can exacerbate sweating episodes, particularly in primary hyperhidrosis.
Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis
The symptoms of hyperhidrosis vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive sweating in specific areas (hands, feet, underarms, face)
- Damp or soaked clothing
- Skin irritation or infections in areas with excessive sweating
- Embarrassment or social anxiety due to sweating
- Difficulty performing daily activities due to sweating
Diagnosing Hyperhidrosis
Diagnosing hyperhidrosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specific tests to rule out other potential causes of excessive sweating. The following steps may be taken during the diagnostic process:
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will ask about symptoms, their frequency and severity, and any potential triggers or underlying conditions.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may help identify areas of excessive sweating.
- Sweat Tests: Tests like the Starch-Iodine Test (where a starch-iodine solution is applied to the skin to visualize sweating) or Gravimetry (measuring the amount of sweat produced over a specific period) may be conducted.
- Additional Testing: If secondary hyperhidrosis is suspected, further testing may be required to identify any underlying medical conditions.
Treatment Options for Hyperhidrosis
Several treatment options are available for managing hyperhidrosis, depending on its severity and type. Options may include:
1. Topical Treatments
- Antiperspirants: Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can help reduce sweating. These are typically applied to the affected areas.
2. Oral Medications
- Anticholinergics: Medications that block the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine can help reduce sweating. However, they may have side effects, including dry mouth and blurred vision.
3. Botulinum Toxin Injections
- Botox: Injections of botulinum toxin can temporarily block the nerves that cause sweating. This treatment is particularly effective for underarm sweating and may also be used for sweating of the hands and feet.
4. Iontophoresis
- Iontophoresis: This non-invasive treatment involves using a device that passes a mild electrical current through water and into the skin's surface, which can help reduce sweating in the hands and feet.
5. Microwave Therapy
- Microwave Treatment: This procedure uses microwave energy to destroy sweat glands in the underarms, providing a longer-lasting solution for excessive sweating.
6. Surgical Options
- Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy (ETS): In severe cases of hyperhidrosis that do not respond to other treatments, surgical intervention may be considered. ETS involves cutting the nerves that trigger sweating, but it carries risks and potential complications.
Coping Strategies for Hyperhidrosis
Living with hyperhidrosis can be challenging, but several strategies can help manage the condition and improve quality of life:
1. Clothing Choices
- Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics that wick moisture away from the skin.
- Dark colors and patterns can help camouflage sweat stains.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid triggers that exacerbate sweating, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and stress.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, to help manage stress.
3. Personal Hygiene
- Maintain good hygiene to reduce the risk of skin irritation and infections.
- Shower regularly and use antibacterial soap to help control odor.
4. Support Groups
- Consider joining a support group or seeking counseling to connect with others who understand the challenges of hyperhidrosis.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is a condition that can significantly impact daily life and emotional well-being. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. If you suspect you have hyperhidrosis, consult a healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and explore the most appropriate treatment options. With proper care and support, individuals with hyperhidrosis can lead fulfilling lives without being held back by excessive sweating.





Comments