Introduction
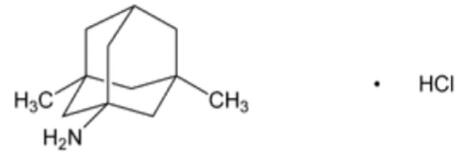
Memantine hydrochloride is a white or almost white powder with the chemical name 1-amino-3,5-dimethyladamantane hydrochloride. It is the hydrochloride salt of memantine, a low-affinity, voltage-dependent, noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist used in the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease (AD). The structure is shown in fig. 1.
Application in the treatment of AD
In 2003, memantine hydrochloride was approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe AD. More information is as follows.
- Introduction of AD
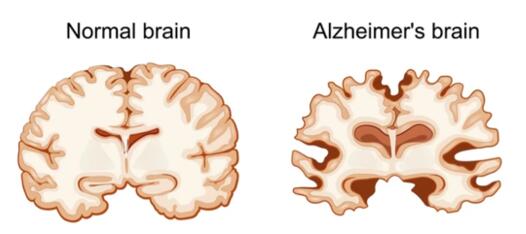
AD is a degenerative brain disease and the main cause of dementia. The most common early symptom of AD is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms may include language disorders, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral problems. The development of AD is associated with environmental and genetic risk factors. The strongest risk factors for AD are advanced age (older than 65 years, although this is not a fixed definition) and carrying at least one APOE ε4 allele[1]. Other risk factors include a head injury history, clinical depression, and hypertension. AD is a threat to human health. It is estimated that someone in the United States now develops AD every 66 seconds. By 2050, a new AD case is expected to occur every 33 seconds, resulting in nearly 1 million new AD cases every year. Memantine hydrochloride is an effective active pharmaceutical ingredient for the treatment of AD[2].
- Mechanism of action
Glutamate can induce the continuous activation of the NMDA receptors in the central nervous system. Due to the excitatory property of glutamate, this overactivation can cause neurotoxicity, which is related to some symptoms of AD. Memantine hydrochloride is a NMDA receptor antagonist that binds to the NMDA receptors to decrease their activation. In addition, this binding inhibits the prolonged influx of Ca2+, particularly from extra-synaptic receptors, which form the basis of neurotoxicity. In this way, memantine hydrochloride potentially enhances the cognitive function of patients with AD.
- Side effects
Common side effects of memantine hydrochloride mainly include:
Confusion
Insomnia
Drowsiness
Dizziness
Agitation
Headache
Hallucinations
Less common side effects of memantine hydrochloride mainly include:
Vomiting
Hypertonia
Anxiety
Increased libido
Cystitis




Comments