Lipomas are benign tumors composed of fatty tissue that can develop anywhere on the body. They are typically soft, movable, and painless, making them often more of a cosmetic concern than a medical one. Despite their generally harmless nature, understanding the essential facts about Lipoma Treatment in Dubai is crucial for those affected. This article delves into the various treatment options available, the process of treatment, and what patients should know to make informed decisions about their care.
Understanding Lipomas
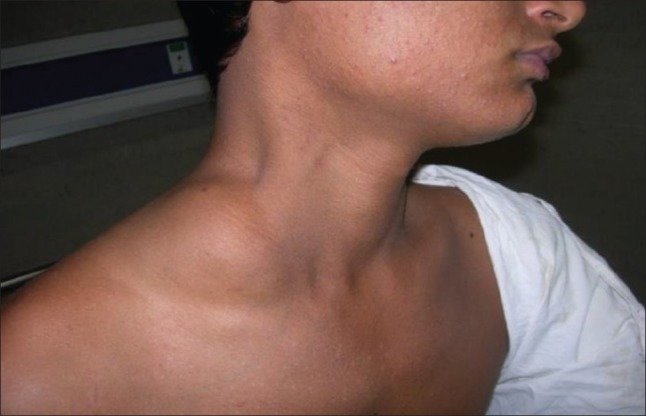
A lipoma is a slow-growing, benign tumor that arises from the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. They are the most common type of soft-tissue tumor in adults. Lipomas are usually small, but they can grow over time. They are characterized by their soft, rubbery texture and can range in size from a few centimeters to several inches in diameter. Lipomas are typically diagnosed through physical examination and imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, which help to assess their size and depth.
When to Seek Treatment
While lipomas are generally not dangerous, they may require treatment if they cause discomfort, interfere with movement, or if there is a cosmetic concern. Additionally, if a lipoma changes in size, shape, or texture, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions. Treatment options vary based on the lipoma's size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal is the most common and definitive treatment for lipomas. This procedure involves excising the lipoma from the body. Surgery is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day. The procedure usually involves a local anesthetic to numb the area, making it relatively straightforward and well-tolerated.
Types of Surgical Procedures:
- Excision: This is the most common approach. The surgeon makes an incision over the lipoma and removes it in its entirety. The incision is then closed with sutures. This method is effective for most lipomas and minimizes the risk of recurrence.
- Liposuction: For some lipomas, especially those that are larger or located in areas where traditional surgery might be challenging, liposuction can be used. This technique involves inserting a thin tube (cannula) into the lipoma to suction out the fatty tissue. While this method can be less invasive, it may not remove the lipoma completely in some cases, which could lead to recurrence.
- Laser Surgery: In certain cases, laser surgery may be used to treat lipomas. This technique uses concentrated light beams to break down fatty tissue. It is less common than traditional surgical methods but can be effective for specific types of lipomas.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
In addition to traditional surgery, there are minimally invasive techniques available that can offer benefits such as reduced recovery time and less scarring.
1. Steroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections can be used to reduce the size of the lipoma. The steroids help to break down the fatty tissue, leading to a reduction in the lipoma’s size. While this method can be effective for some patients, it may not completely eliminate the lipoma and may require multiple treatments.
2. Radiofrequency Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation involves using radio waves to heat and destroy the fatty tissue. This technique is less invasive than traditional surgery and can be performed under local anesthesia. It is a newer option and may not be suitable for all lipomas, but it can be effective in certain cases.
Post-Treatment Care
After treatment, it is essential for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
- Wound Care: If the lipoma is removed surgically, keeping the wound clean and dry is crucial. Patients should follow any specific instructions regarding wound care, including changing dressings and avoiding activities that could disrupt the healing process.
- Pain Management: Some discomfort and swelling are normal after treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers or medications prescribed by the healthcare provider can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor the healing process and ensure that the lipoma has been completely removed. During these visits, the healthcare provider will assess the area and address any concerns.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients may be advised to avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting for a period following the treatment. This helps to prevent complications and ensures optimal healing.
Potential Complications
While lipoma treatments are generally safe, like any medical procedure, they carry some risk of complications. These can include:
- Infection: Though rare, infections can occur at the site of surgery. Proper wound care and following medical advice can minimize this risk.
- Recurrence: In some cases, the lipoma may recur if it was not completely removed. Regular follow-up with the healthcare provider can help detect and address any recurrence early.
- Scarring: Surgical removal can result in scarring. The extent of scarring varies depending on the size and location of the lipoma and the surgical technique used.
- Nerve Damage: Although uncommon, there is a slight risk of nerve damage during surgery, which can lead to numbness or tingling in the surrounding area.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
While lipomas are benign, their appearance and the need for treatment can affect a person’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. It is important for patients to address any concerns they may have about the cosmetic aspects of lipoma removal with their healthcare provider. Support from family, friends, or counseling services can also be beneficial in managing the emotional impact of the condition and its treatment.
Choosing the Right Treatment
Deciding on the most appropriate treatment for a lipoma involves considering several factors:
- Size and Location: Larger lipomas or those located in challenging areas may require different treatment approaches compared to smaller, more accessible lipomas.
- Health Status: A patient’s overall health and any underlying medical conditions can influence the choice of treatment. It is essential to discuss these factors with a healthcare provider.
- Personal Preferences: Patients may have preferences regarding the type of treatment based on their lifestyle, concerns about scarring, and recovery time. It is important to discuss these preferences with a healthcare provider to find the best option.
Conclusion
Lipomas, though generally benign, may require treatment based on their size, location, and the impact they have on a person’s well-being. Understanding the available treatment options, the process involved, and potential complications can help patients make informed decisions about their care. Whether through traditional surgical removal, minimally invasive techniques, or ongoing management, the goal is to address the lipoma effectively while minimizing risks and ensuring a positive outcome. For anyone dealing with a lipoma, working closely with a healthcare provider and following recommended care guidelines can lead to successful treatment and improved quality of life.




Comments