Lung cancer is a severe and often life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding lung cancer's signs, types, stages, screening, diagnosis, treatment, causes, and prognosis is crucial for early detection and effective management. Lung cancer treatment therapy options vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, highlighting the importance of personalized care and multidisciplinary approaches.
Here is everything you need about lung cancer to empower you with knowledge and awareness.
1. Signs of Lung Cancer:
The symptoms of lung cancer might differ based on the stage and kind of disease. Common symptoms include continuous coughing, coughing up blood, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, exhaustion, and repeated respiratory infections. It's important to note that some individuals may not experience any symptoms in the early stages of lung cancer, underscoring the importance of regular screenings for those at high risk.
2. Types of Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer is divided into two categories: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer. NSCLC is the most common kind of lung cancer, accounting for more than 85% of all cases, and it has several subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and giant cell carcinoma. SCLC is less prevalent but develops and spreads more quickly than NSCLC.
3. Stages of Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer is classified according to the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to neighboring lymph nodes, and if it has metastasized to other areas of the body. Stages vary from 0 (carcinoma in situ) to IV (advanced cancer that has spread to other organs). Staging helps identify the best therapy and prognosis for those who have been diagnosed with lung cancer.
4. Screening and Diagnosis:
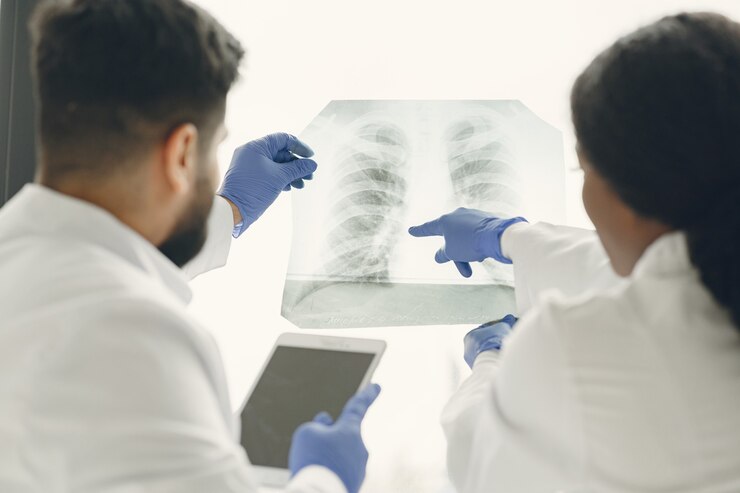
Screening for lung cancer involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and sputum cytology (examining mucus from the lungs for cancer cells). A biopsy is a diagnostic process in which a tiny tissue sample is extracted and examined under a microscope to confirm the existence of cancer cells and establish the type and stage of lung cancer.
5. Treatment of Lung Cancer:
Treatment options for lung cancer vary according to the kind, stage, and general health of the patient. Common treatments include tumor removal surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy (the use of drugs to target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells), immunotherapy (the stimulation of the body's immune system to fight cancer), and palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
6. Causes of Lung Cancer:
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, accounting for the overwhelming majority of cases. Other risk factors include secondhand smoking, environmental contaminants (e.g., radon, asbestos, and certain chemicals), genetics, and a family history of lung cancer. It is crucial to highlight that not all persons with risk factors acquire lung cancer, and some lung cancer patients have no recognized risk factors.
7. Prognosis of Lung Cancer:
The prognosis of lung cancer is determined by several factors, including the stage upon diagnosis, the kind of lung cancer, the patient's general condition, and the efficacy of therapy. Unfortunately, lung cancer is frequently identified at an advanced stage after it has spread to other regions of the body, making treatment more complicated. However, advances in screening, diagnosis, and treatment have improved outcomes for many patients with lung cancer.
In conclusion, lung cancer is a complex and challenging disease that requires comprehensive understanding and management. merging therapies such as hyperthermia cancer treatment show promise in complementing traditional treatments and improving patient outcomes.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms, understanding the different types and stages, undergoing regular screenings for those at high risk, seeking prompt medical attention for diagnosis and treatment, avoiding known risk factors such as smoking, and advocating for lung cancer awareness and research are all critical steps in combating this disease and improving outcomes for patients.




Comments