Understanding Hemangiomas
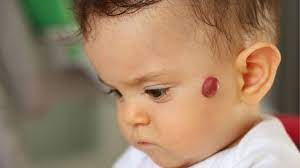
Hemangioma is a vascular growth that often appears shortly after birth. These benign tumors are comprised of an abnormal collection of blood vessels. While they are typically harmless, certain types of hemangiomas can cause complications, such as obstruction of vision, breathing difficulties, or disfigurement if located on the face or neck.
Types of Hemangiomas
- Infantile Hemangiomas: These are the most common type, appearing within the first few weeks of life. They tend to grow rapidly during the first year before gradually shrinking over several years.
- Congenital Hemangiomas: Unlike infantile hemangiomas, congenital hemangiomas are fully formed at birth and do not typically grow rapidly.
- Deep Hemangiomas: These grow deeper into the skin and may not be visible on the surface. They can be more challenging to diagnose and treat.
Hemangioma Treatment Options
Treatment for hemangiomas depends on various factors, including the size, location, and potential complications associated with the growth. While many hemangiomas require no treatment and will eventually resolve on their own, others may necessitate medical intervention.
1. Observation
In cases where the hemangioma is small and not causing any complications, a "wait-and-see" approach may be recommended. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to track any changes in size or appearance.
2. Medication
Certain medications, such as beta-blockers or corticosteroids, may be prescribed to help shrink the hemangioma or prevent further growth. These drugs are typically administered orally or via injection.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy can be effective in treating superficial hemangiomas by targeting the blood vessels that feed the growth. This minimally invasive procedure is often used to reduce the size and appearance of the hemangioma.
4. Surgical Removal
In cases where the hemangioma poses a significant risk or causes severe complications, surgical removal may be necessary. This option is usually considered when other treatments have failed or are not suitable for the patient.
Hemangioma Insurance Coverage
Navigating insurance coverage for hemangioma treatment can be complex, as policies and coverage vary depending on the insurance provider and individual plan. However, many insurance plans do offer coverage for medically necessary treatments for hemangiomas.
1. Preauthorization
Prior authorization from the insurance company may be required before certain treatments, such as surgical removal or laser therapy, can be performed. This involves obtaining approval from the insurer to ensure that the treatment is deemed medically necessary.
2. In-Network Providers
Using in-network healthcare providers can help minimize out-of-pocket expenses, as these providers have negotiated rates with the insurance company. It's essential to verify whether the treating physician and facility are within the insurance network.
3. Coverage Exceptions
While most insurance plans cover medically necessary treatments for hemangiomas, there may be exceptions or limitations to coverage. It's crucial to review the terms of the insurance policy and consult with the insurer if there are any questions or concerns about coverage.
4. Appeals Process
If a claim for hemangioma treatment is denied by the insurance company, patients have the right to appeal the decision. This involves submitting additional documentation or evidence to support the medical necessity of the treatment.
Conclusion
Hemangioma Treatment in Riyadh is a common vascular growth that can vary in size and severity. While many hemangiomas require no treatment and will resolve on their own, others may necessitate medical intervention to prevent complications. Understanding the available treatment options and navigating insurance coverage are essential steps in managing hemangiomas effectively. By working closely with healthcare providers and insurance companies, patients can access the necessary care and treatment for this condition.





Comments