Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing lung cancer:
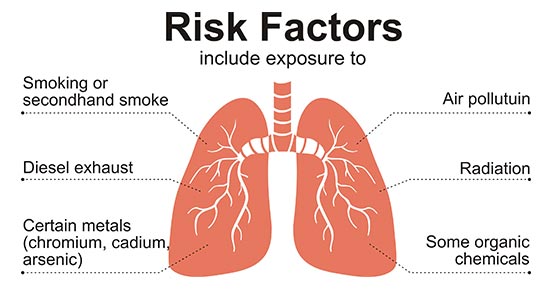
- Smoking: This is the leading cause of lung cancer. Cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking all increase risk. Secondhand smoke exposure is also a significant risk factor.
- Exposure to Radon: Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and buildings, especially in areas with certain types of soil or rock. Prolonged exposure to high levels of radon increases lung cancer risk.
- Exposure to Asbestos and Other Carcinogens: Occupational exposure to asbestos, arsenic, chromium, nickel, and other carcinogens can significantly increase the risk of lung cancer, especially among smokers.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of lung cancer are at higher risk, indicating a potential genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to air pollution, such as that from vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and other sources, can increase lung cancer risk.
- Personal History of Lung Disease: People with a history of certain lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or tuberculosis, have an increased risk of lung cancer.
- Radiation Therapy to the Chest: Previous radiation therapy to the chest, typically for other types of cancer, can increase the risk of developing lung cancer later in life Best Pulmonologist in Sodala .
- Dietary Factors: Some studies suggest that a diet low in fruits and vegetables but high in red and processed meats may increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Certain Genetic Factors: While less common, certain genetic mutations or conditions, such as mutations in the EGFR gene, are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
- Gender and Age: Lung cancer is more common in older adults and in males, although the gap has been narrowing in recent years.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices and healthcare.




Comments