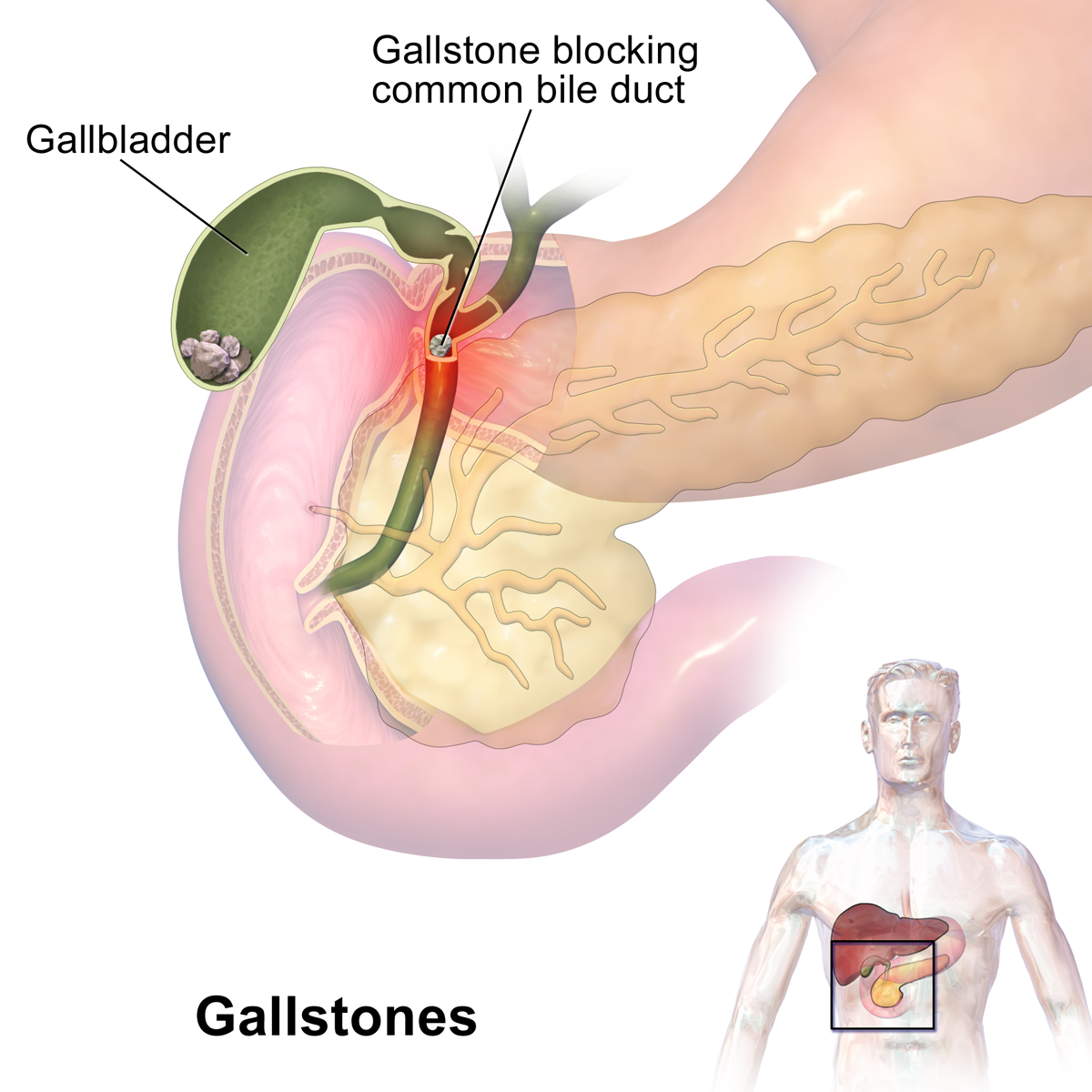
everal risk factors contribute to the development of gallbladder stones (also known as gallstones). These include:
1. Gender: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men, especially those who are pregnant, on hormone replacement therapy, or taking birth control pills.
2. Age: Gallstones are more common as people age, particularly after the age of 40.
3. Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of gallstones, as excess body weight can lead to increased cholesterol in bile, which can form stones Gallbladder Stone in Jaipur.
4. Rapid weight loss: Losing weight very quickly, whether through dieting, bariatric surgery, or illness, can increase the risk of gallstones.
5. Diet: Diets high in cholesterol and low in fiber may increase the risk of gallstones. Similarly, diets high in refined carbohydrates and sugar can contribute to gallstone formation.
6. Family history: If other members of your family have had gallstones, you are at higher risk.
7. Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as Native Americans and Mexican Americans, are at higher risk for gallstones.
8. Medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, and certain blood disorders can increase the risk ofGallbladder Stone in Jaipur.
9. Certain medications: Use of medications that lower cholesterol levels in the blood, such as fibrates, can increase the amount of cholesterol in bile and thus the risk of gallstones.
10. Gallbladder problems: Conditions that affect the gallbladder, such as inflammation (cholecystitis) or reduced emptying (biliary dyskinesia), can increase the risk of gallstones.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase the likelihood of developing gallstones, not everyone with these risk factors Gallbladder Stone in Jaipur will necessarily develop them.




Comments