Laparoscopic surgery differs from traditional (open) surgery in several key ways:
Incisions and Access
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
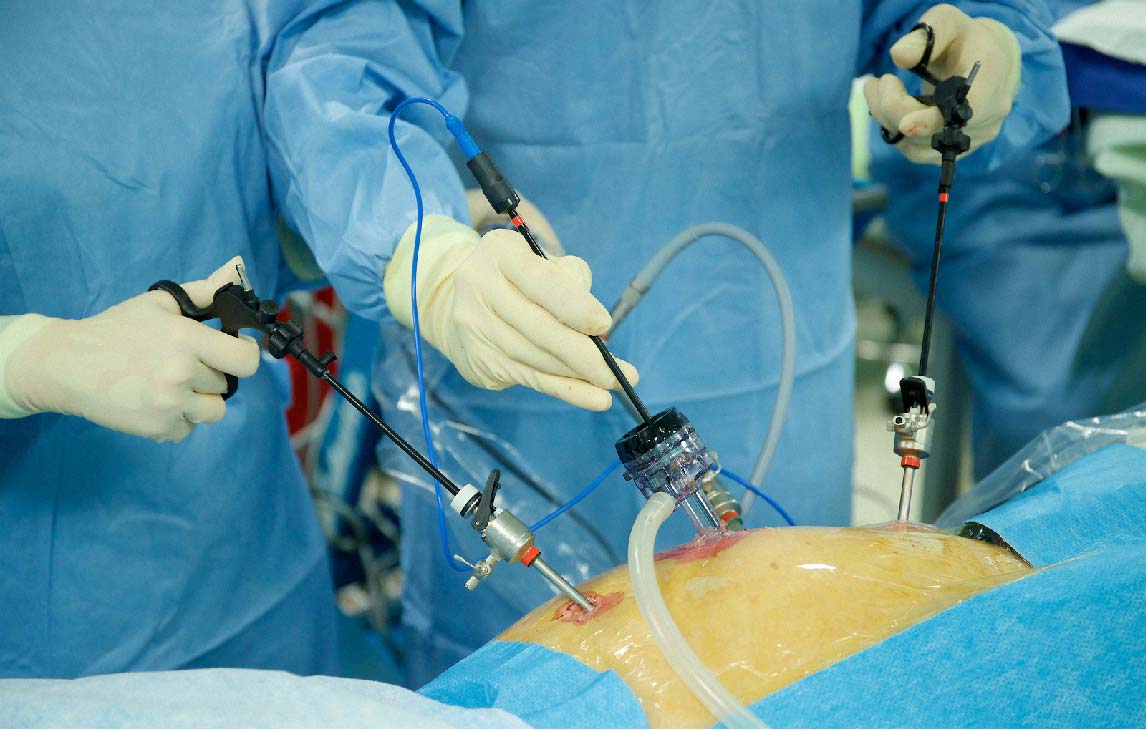
— Involves making several small incisions, typically 0.5 to 1.5 cm in length.
— A laparoscope (a long, thin tube with a high-resolution camera and light) is inserted through one of the incisions.
— Surgical instruments are inserted through other small incisions.
- Traditional Surgery:
— Requires a larger incision to access the surgical area, often several inches long.
— The larger opening allows direct access and visualization of the organs and tissues.
Visualization
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
— The camera on the laparoscope projects a magnified view of the internal organs onto a monitor, providing the surgeon with a detailed and clear view of the operating field.
- Traditional Surgery:
— The surgeon views the internal organs directly through the large incision.
Technique and Instruments
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
— Surgeons use specialized long, thin instruments designed for manipulation and cutting within the confined space of the body.
— Precision is enhanced by the magnified video feed, allowing for meticulous movements.
- Traditional Surgery:
— Surgeons use standard surgical instruments and have direct tactile feedback from the tissues they are manipulating.
Tissue Handling and Trauma
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
— Minimizes trauma to the surrounding tissues and organs due to smaller incisions and precise movements.
— Reduced risk of blood loss and postoperative complications.
- Traditional Surgery:
— Involves more extensive tissue manipulation and potentially greater trauma to surrounding structures.
Recovery and Outcomes
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
— Generally results in less postoperative pain, quicker recovery times, shorter hospital stays, and smaller scars.
— Lower risk of infections and complications.
- Traditional Surgery:
— Typically associated with longer recovery periods, more postoperative pain, larger scars, and higher risk of complications such as infections.
Versatility and Applications
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
— Highly versatile and can be used for a wide range of procedures, including those involving the abdomen, pelvis, and thoracic cavity.
— Increasingly used for complex surgeries due to advancements in technology and techniques.
- Traditional Surgery:
— Still necessary for certain complex or emergency situations where immediate and extensive access is required.
These differences make laparoscopic surgery a preferred option for many procedures due to its minimally invasive nature and associated benefits.




Comments