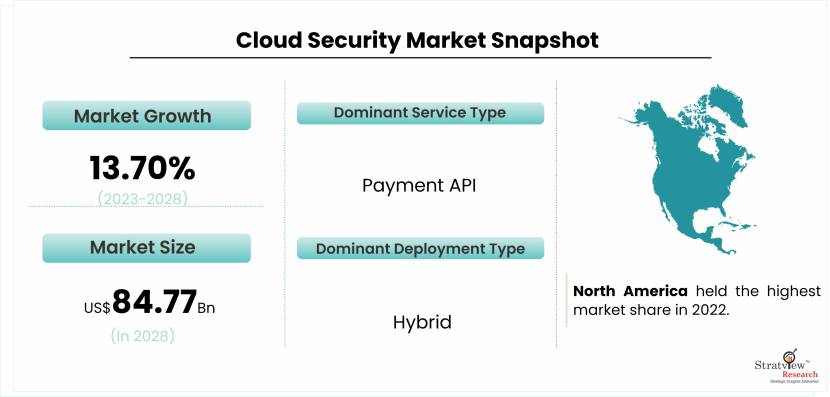
The rapid growth of cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses store, process, and manage data. Cloud services offer unparalleled convenience, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making them a popular choice for organizations worldwide. However, this digital transformation has also raised significant data privacy concerns, as sensitive information moves beyond the confines of traditional data centers. In this article, we will explore the key data privacy concerns in the cloud security market and discuss strategies to address them. The cloud security market is projected to grow from USD 39.03 billion in 2022 to USD 84.77 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 13.70% during the forecast period.
Data Privacy Concerns in the Cloud Security Market
Data Breaches and Cyberattacks: Data breaches have become a prevalent threat in the cloud security landscape. Hackers and cybercriminals constantly exploit vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure to gain unauthorized access to valuable data. High-profile data breaches have exposed personal and sensitive information, eroding public trust in cloud services.
Lack of Control and Visibility: Entrusting data to third-party cloud providers may lead to a perception of reduced control and visibility over the data. Organizations might fear losing control over their sensitive information and not knowing how the data is being handled by the cloud service provider.
Data Residency and Sovereignty: Some regions and industries have strict regulations concerning data residency and sovereignty. Data may need to remain within specific geographical boundaries due to legal and compliance requirements. Businesses might worry about their data being stored or processed in locations that conflict with these regulations.
Cloud Provider Security Standards: The security practices and standards of cloud service providers can vary significantly. Businesses may have concerns about the level of security implemented by their chosen provider and whether it aligns with industry best practices and compliance requirements.
Compliance with Data Regulations: Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, impose strict requirements on data handling and protection. Ensuring compliance with these regulations in the cloud environment can be challenging and requires a clear understanding of responsibilities and obligations.
Addressing Data Privacy Concerns
Encryption and Secure Protocols: Cloud providers should offer robust encryption mechanisms to protect data both in transit and at rest. Strong encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and useless to unauthorized parties.
Data Classification and Access Controls: Implementing data classification policies helps identify the sensitivity of information and allows organizations to apply appropriate access controls. Access controls limit data access to authorized personnel only, reducing the risk of unauthorized exposure.
Transparency and Auditability: Cloud service providers should offer transparency regarding their security practices and data handling procedures. Regular audits and assessments of security controls can instill confidence in customers that their data is being protected effectively.
Data Residency Options: Cloud providers should offer data residency options to address concerns about storing data in specific geographic locations. This can help organizations comply with regional data sovereignty regulations.
Compliance Certifications: Cloud service providers should obtain relevant compliance certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, to demonstrate their commitment to security and adherence to industry standards.
Incident Response and Reporting: Clearly defined incident response protocols and timely reporting of security incidents are essential to maintaining trust with customers. A proactive and transparent approach to handling incidents can mitigate the impact of potential breaches.
Customer Education: Cloud providers should educate their customers about best practices for securing their data in the cloud. Providing resources, training, and guidelines can empower organizations to take an active role in protecting their data.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies: Diversifying the cloud infrastructure through multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies can mitigate risks associated with relying on a single cloud provider. Distributing data across different clouds can enhance data redundancy and resilience.
Conclusion
Addressing data privacy concerns in the cloud security market is a shared responsibility between cloud service providers and their customers. While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, organizations must remain vigilant about data protection and privacy. By implementing strong encryption, access controls, transparency, and compliance measures, cloud service providers can gain their customers' trust and demonstrate their commitment to data privacy. Simultaneously, businesses must actively engage in understanding their cloud providers' security practices and take appropriate measures to protect their data throughout its lifecycle in the cloud. A collaborative effort between cloud providers and their customers is essential to create a secure cloud environment that respects data privacy and fosters confidence in the digital age.




Comments